Basic improvement (Kaizen)
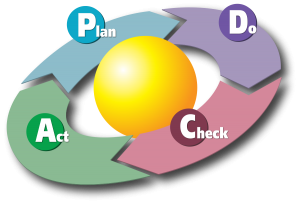
Kaizen is a Japanese word combined by ‘kai’ – ongoing and ‘zen’ – improvement, translated into English term “ongoing improvement”. This is a famous Japanese business philosophy where all employees from all parts of the business will work together to achieve common goals, improve production. Some statistics on Kaizen initiative at world-famous corporations:
- Toyota: 10-12 ideas/employee/year
- Suzuki: 50,000 ideas/year
- Toyota Lexus: 100 ideas/employee/year
The improvement processes in Kaizen are small, incremental, but deliver impressive results for a long time. That is the secret to the success of Japan’s largest corporations. The “Kaizen” course will create a strong driving force for production in enterprises.

COURSE OVERVIEW
Name of the course: Basic improvement (Kaizen)
Object: Employees, workers, and interns
Training time: 2 – 3 days (designed as customer’s requirements)
Language: Vietnamese
Lecturers: Vietnamese
Forms of training: Inhouse or Public workshop
Training methods: Lecture presentation, discussion, and practice are organized in the classroom
PURPOSE OF COURSE
- Understanding the purpose, significance, and importance of innovation to sustainable development
- Knowing how to improve from the simplest things but with better efficiency.
- Being awareness of the thinking of every-day improving.
TRAINING CONTENT IN THE COURSE
1. Factory Basics
- Management of QCDMSE factors
- Management of 4M
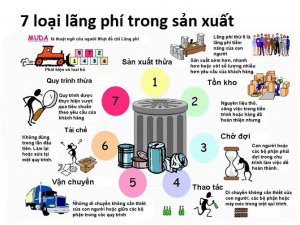
2. Muri-Mura-Muda and 7 wastes
- Overview of Muri-Mura-Muda
- Method of determining 7 wastes in production
3. Squander topic selection methodology
- 3Mu in production line/process and description by flowchart
- Determining the actual timing of all stages in the line or process and identifying stages of interest
- Identifying 3Mu at the stage/work of interest and selecting the topic
- Practice: Identifying squanders topics
4. Capturing the current status
- Understanding detailed maneuvers and clarifying the Muda(s)
- Standard work coordination table: human-machine work coordination analysis
- Simultaneous-motion cycle chart: SIMO
- Transport process analysis chart
- 2-handed analysis chart
- Therblig analysis: Muri, Mura, motion, machining squander
- 5W-2H Tools
- Practice: Capturing the current status
5. Analysis of the current status
- 3M and finding possible problem points
- Verifying unclear problem points (4M)
- Practice: Situation analysis
6. Analysis of the cause
- What is the root cause?
- Applying 5Whys to find the root cause
- Practice: Analysis of the Root Cause
7. Choosing counterparts
- Proposing as many potential countermeasures as possible
- Building consensus with stakeholders and choose a countermeasure
- Practice: Determining the countermeasure
8. Confirming the results
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the topic
- The visible effect, the invisible effect and the economic efficiency of the topic
- Practice: Evaluating the effectiveness of the topic
9. Standardization and eye management
- Purpose and meaning of standardization and eye management
- Practice: Identifying points to be standardized in your topic.
FEEDBACK
"The course has the most useful knowledge I have ever learned."
"All valuable knowledge."
“The Kaizen business philosophy has been successfully applied in many big companies in Japan (Toyota, Canon, Honda, ...) and is increasingly trusted in other countries, including Vietnam."