Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
TPM – Total Productive Maintenance is the maintenance overall. That is, assign basic maintenance tasks such as inspections, cleaning, lubricating, and simple adjustments to production team members.
TPM requires the participation of all members of the factory and company to work together to eliminate problems that reduce the efficiency of machines and equipment.
This gives maintenance team members time to focus on planned equipment maintenance, equipment improvements, training, and other valuable activities.
Sign up for the course “Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)” to learn more about the method widely applied by businesses in the industrial manufacturing sector around the world

COURSE OVERVIEW
PURPOSE OF COURSE
- Clearly understand the purpose and importance of Total Productive Maintenance to maximize productivity and quality
- Well operate the system of daily inspection, maintenance, periodic maintenance to ensure the equipment runs smoothly and generates maximum productivity
TRAINING CONTENT IN THE COURSE
Overall of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
- Definition of TPM
- What is the principle of TPM?
- What is the purpose of implementing the TPM?
The importance of TPM to PQCDMSE
- The benefits from the implementation of TPM
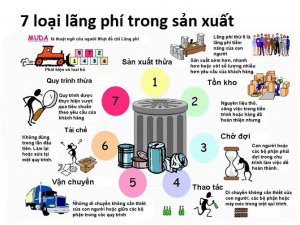
- Losses during equipment operation
OEE and Loss Index
- How to calculate the OEE index?
- What is the basic goal of the TPM?
- Practice 1: Calculate the OEE index at the workplace
Five pillars of TPM
- What are the main activities of the TPM?
- 5 pillars of the TPM
- Steps to implement the TPM
- Practice 2: Evaluate the implementation of the TPM pillars at the workplace
Self-managed maintenance
- What is self-managed maintenance?
- Requirements for self-operated workers
- 7 standard steps of self-operated maintenance
- Practice 3: Define the maintenance items the operator can do on their own at the equipment location they are in charge of.
Define the program of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
- Develop policy guidelines for TPM activities
- Develop implementation plan for TPM
- Establish self-managed maintenance groups by region/division
- Selection of sample region for TPM implementation (self-managed maintenance improvement and standardization)
- Develops the skills required over time for the self-managed maintenance worker and the maintenance department
Course review, action plan and certification
FEEDBACK