Logical thinking through problem solving skills
Not everyone knows how to handle unexpected problems that arise in the course of work or life. To adapt well to each circumstance, we have to follow the process and equip the most effective problem-solving skills.
- So what is a problem-solving skill?
- What are the factors affecting problem-solving skills?
- What are effective methods to solve the problems?
- And, how to improve problem-solving skills?
The course “Logical thinking through problem–solving skills” will answer all of these questions!

COURSE OVERVIEW
Name of the course: Logical thinking through problem solving skills
Object: Deputy department, managers, supervisors, group leaders, etc.
Training time: 2 – 3 days (designed as customer’s requirements)
Language: Vietnamese
Lecturers: Vietnamese
Forms of training: Inhouse or Public workshop
Training methods: Lecture presentation, discussion, and practice are organized in the classroom
PURPOSE OF COURSE
- Be logical masterful in the problem-solving process
- Good identification of issues that affect goals
- Analyze the root causes of problems and find out logical as well as thorough solutions
TRAINING CONTENT IN THE COURSE
II. OVERVIEW OF PROBLEM-SOLVING METHODS
- Contents of training
- What is a problem-solving method?
- Overview of steps in the problem-solving methods
- Introduction to one-page-A3 reporting methods
- Examples of problem-solving reports
- Practice
- Learners share the status quo of problem-solving
- Ask and answer questions directly in the classroom
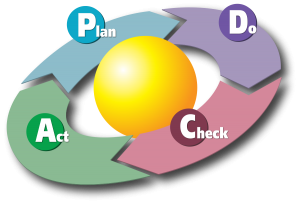
II. STEPS TO SOLVE PROBLEMS
Step 1: Identify problems
- What is a problem?
- Steps to define problems
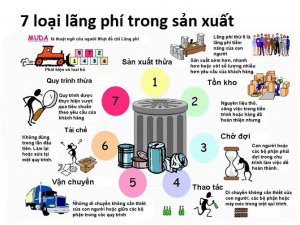
- Identify problems by the QCDMSE, 4M, and 7 wastes factors
- Choose the priority problem to be solved according to S.U.G theory
- Practice 1: Identify current problems at your department/division
Step 2: Understand the status quo
- What is to understand the status quo and its purposes? For example?
- Steps to understand the status quo
- Apply the 3G principle and collect data
- Detail status quo according to 5W-2H
- Determine factors for analysis according to the Pareto principle (80:20)
- Practice 2: Understand the status quo of the problems identified in Practice 1.
Step 3: Analyze status quo
- What is the analysis of the status quo? And what are its purpose? For example?
- Steps to analyze the status quo
- Apply analysis tools such as the 3G principle, historical data collection, comparison, process chain analysis, related-people interview.
- Methods of data collection and verification of problem points
- Practice 3: Analyze the status quo for the identified cases above-mentioned in Practice 2.
Step 4: Analyze root causes
- What is root cause analysis? Anh what are its purposes? For example?
- Steps to perform root cause analysis
- Analytical tools: Brainstorming, causal diagram, and 5-Whys tree diagram
- Methods to verify root causes
- Practice 4: Analyze the root causes of the problem points identified in Practice 3
Step 5: Select the countermeasures
- What are countermeasures and their purposes? For example?
- Steps for selecting the countermeasures
- Temporary and permanent countermeasures, soft countermeasures, and hard countermeasures
- Criteria for selecting the countermeasures are efficiency, cost, and risk
- Consensus building and policy action planning
- Practice 5: Select the countermeasures for the causes identified in Practice 4
Step 6: Confirm results
- What is the result confirmation of countermeasures? What are its purposes? For example?
- Confirm results such as tangible results, intangible results, and economic results
- Compare the results after performing countermeasures against before doing
- If the results do not meet requirements, what need to do next?
- Practice 6: Confirm the assumed results of the countermeasures performed in Practice 5
Step 7: Standardization and visual management
- What is standardization? What are its purposes? For example?
- What and how do you need to standardize after implementing the countermeasures?
- What is visual management? What are its purposes? For example?
- What and How do you need to visualize after implementing the countermeasures?
- Practice 7: Standardize and visually manage the implemented countermeasures
III. COURSE REVIEW, ACTION PLAN, AND CERTIFICATION
FEEDBACK
“Problem-solving skills give you the abilities to handle unexpected difficulties arising during projects as well as in the process of interacting with customers.”
“Problem-solving skills are one of the essential skills in learning and working in our life.”
“Life has so many problems to solve, neither of which is the same and there is no common formula to deal with all of them.”