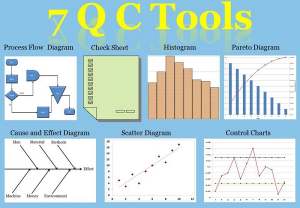
Waste elimination and 7 IE tools
Why should waste be eliminated in production?
- Producing many defective products causes great damage to the company.
- Overproduction gives rise to excessive costs for warehousing, storage costs, manpower costs, equipment costs, etc
- Storage excessive and for a long time causes businesses to not only sink into unproductive assets, but also lead to other costs such as warehous renting, product storage or expenses due to damage, etc
- Errors in paperwork, providing false information about products, delayed delivery, manufacturing the incorrect specifications, excessive use of materials or generating unnecessary scrap, etc cause a lot of waste for the business
- The business knows that there is a lot of waste in production, but the application of waste elimination tools still faces many difficulties.
The course “Waste elimination and 7 IE tools” will help businesses find out problems with improved opportunities to reduce ineffective activities in their own factories and companies.
COURSE OVERVIEW
Name of the course: Waste elimination and 7 IE tools
Object: Employees, workers, interns
Training time: 2 – 3 days (designed as customer’s requirements)
Language: Vietnamese
Lecturers: Vietnamese
Forms of training: Inhouse or Public workshop
Training methods: Lecture presentation, discussion, and practice are organized in the classroom
PURPOSE OF COURSE
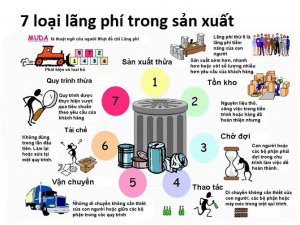
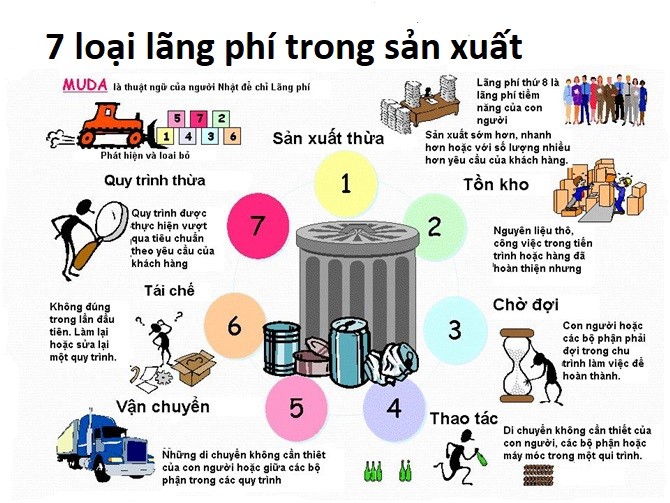
- Correctly identify 7 types of workplace waste
- Apply each IE tool to reduce, eliminate 7 wastes.
- Continuous improvement for a lean and highly productive workplace.
- Build improvement systems throughout the organization.
TRAINING CONTENT IN THE COURSE
Topic 1: Muri-Muda-Mura and 8 types of waste
- What is Muri-Mura-Muda?
- What are the 8 types of waste? (Definition, identification)
- Practice 1: Identify situational waste
Topic 2: Workflow analysis
- What is the San-Gen-Shugi methodology? (Genba ,Genbutsu & Genjitsu- Principle of three realities)
- Determine the actual time of the stages in the production line, or of the working steps in the workflow
- Create a flow chart of work and identify waste
- Practice 2: Process chain analysis and situational waste identification
Topic 3: Table of standard work coordination
- What is Tact time? What is cycle time?
- What is chart of standard work coordination?
- How to chart a standard work coordination and identifying waste
- Practice 3: Chart a standard work coordination and identify situational waste
Topic 4: The analysis chart of SIMO coordinated manipulation
- What is a SIMO chart?
- How to make a SIMO chart
- On-line work, off-line work, adjustment work
- Practice 4: SIMO charting and waste identification
Topic 5: The analytical method of two-handed manipulation
- What is the analysis of two-handed manipulation?
- Analytical method of two-handed manipulation and waste identification
- Practice 5: Analyzing two-handed manipulation, identifying waste
Topic 6: Analysis methods of Therbligs movements
- What is Therblig Analysis?
- 18 types of movements of Therblig analysis
- Practice 6: Analyzing Therblig and identifying waste
Topic 7: Analysis of the transportation process, From-To
- Analysis of the transportation process and what is From-To?
- How to chart to analyse the transportation process
- How to make a chart From – To
- Practice 7: How to chart transportation process, from-to and identify waste
Topic 8: Solutions of waste elimination and minimization
- ECRS solution (Eliminate – Combine – Reorder – Simplify)
- The principle of economic manipulation
- Karakuri method
- The principle of the transportation process
- Pokayoke
- Practice 8: Determine the solutions of eliminating and minimizing situational waste
Course review, action plan and certification
FEEDBACK
“Synthesis of daily waste into new figures clearly sees the problem”
“Just eliminate 6/8of waste was good enough”
“The goal of eliminating all waste in the next 2 years”